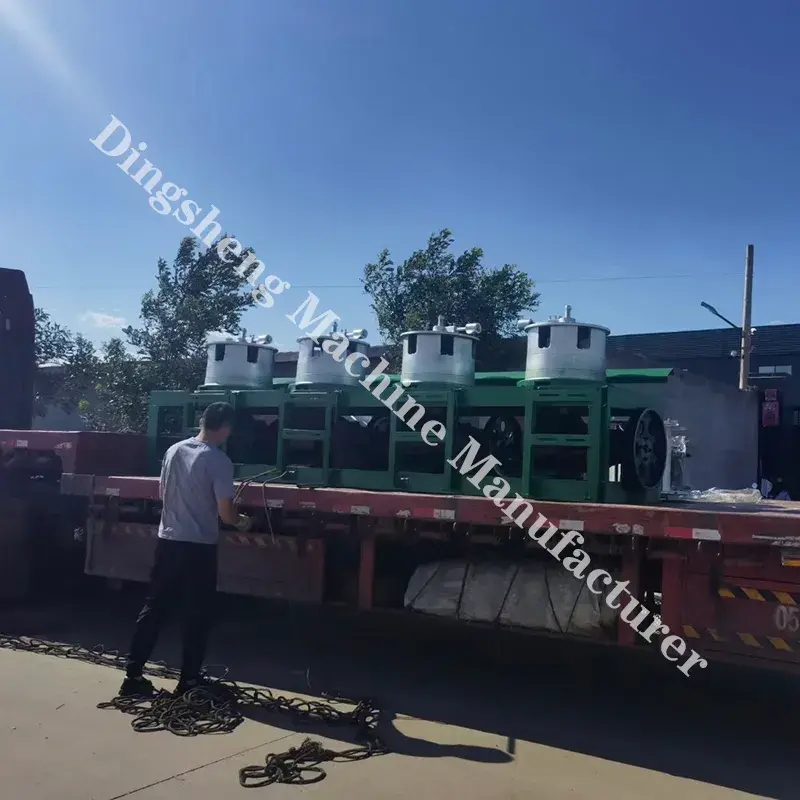
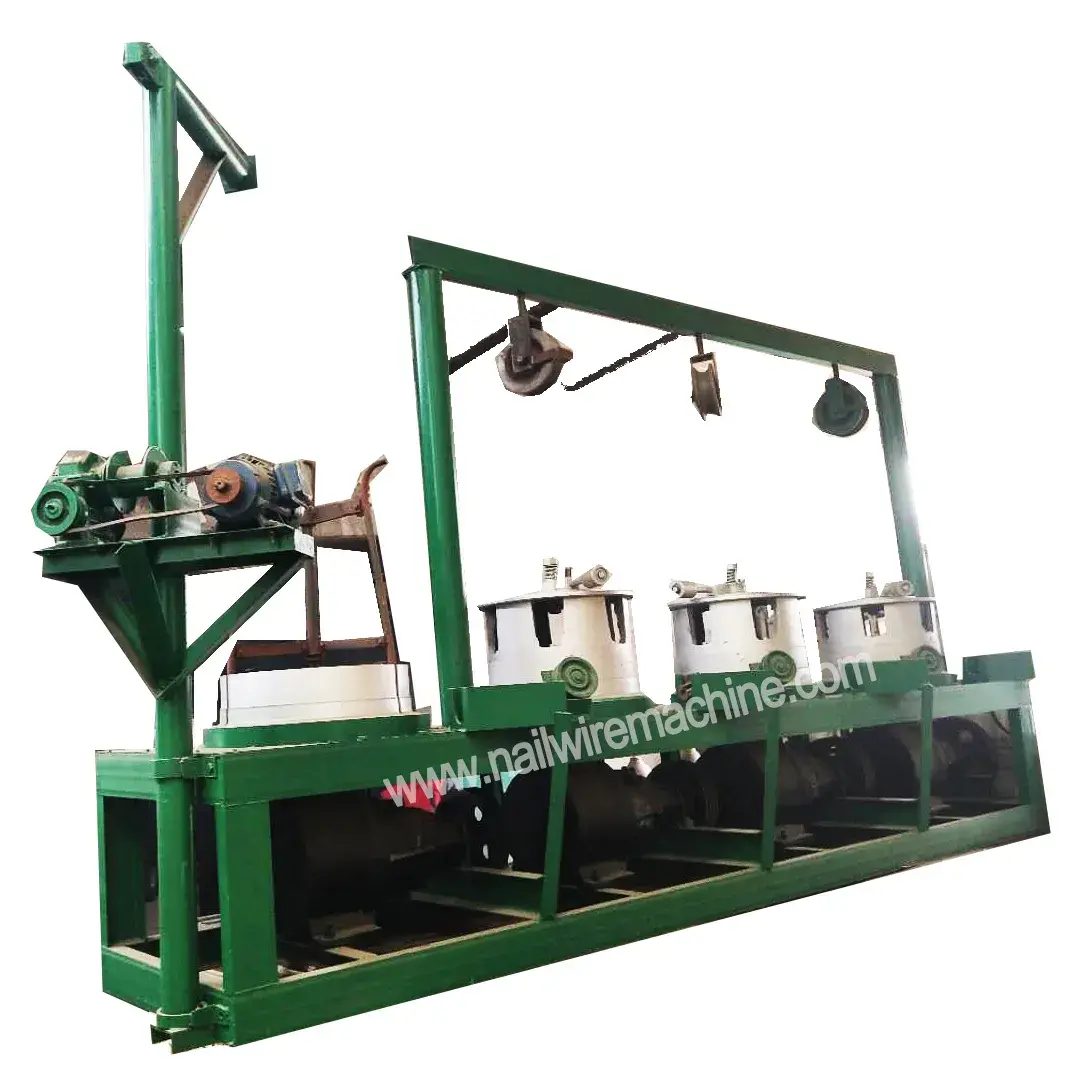
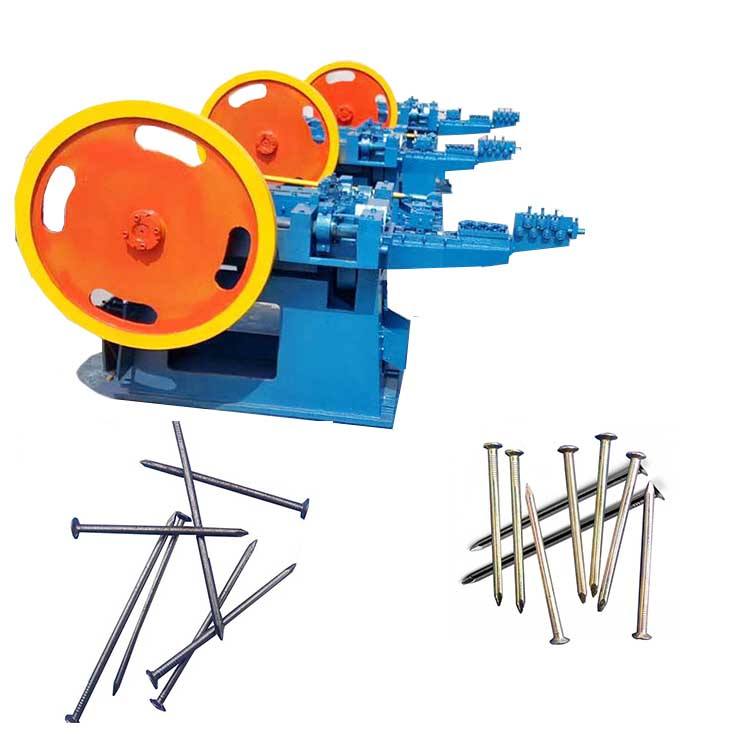
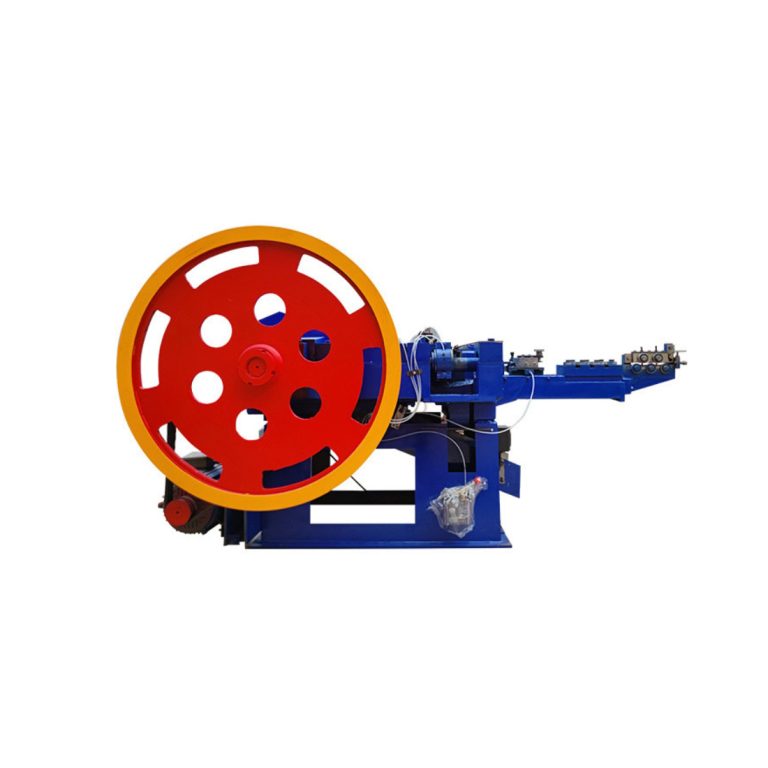
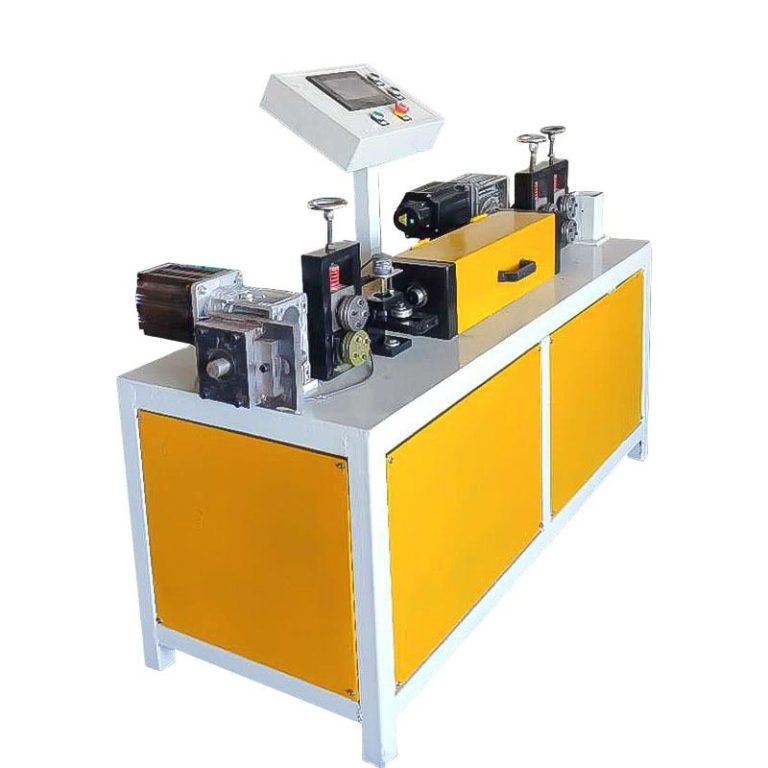
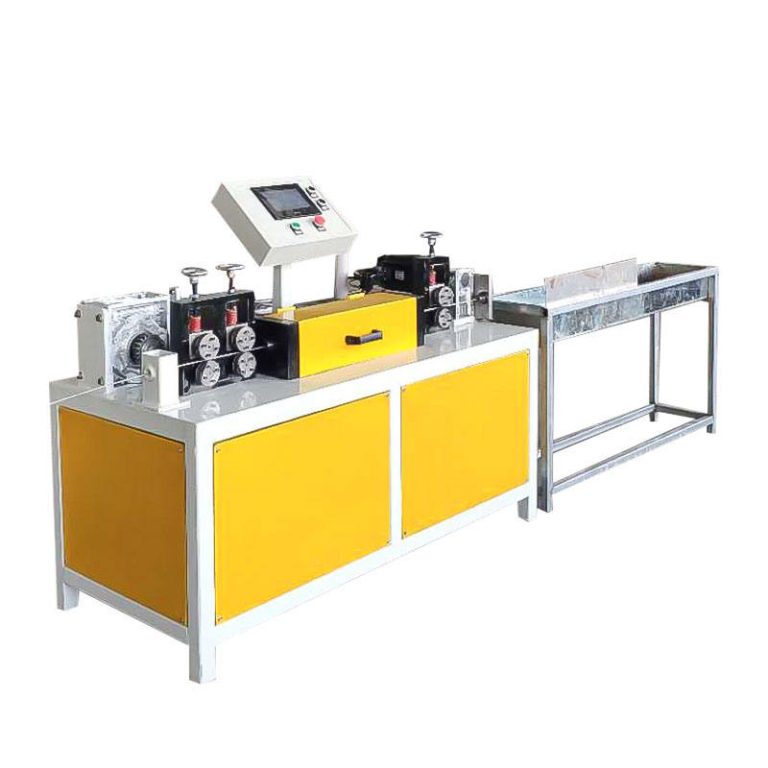
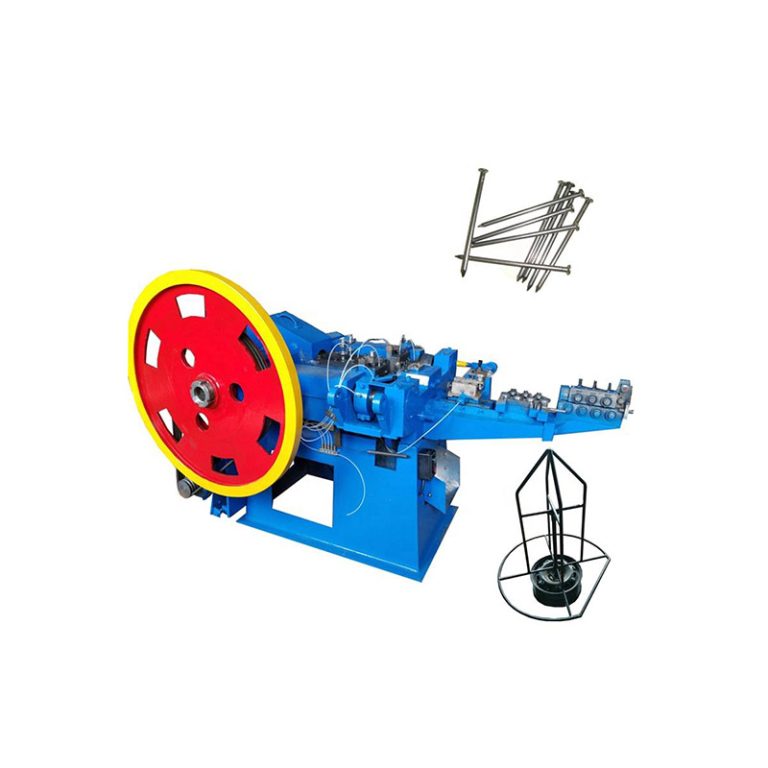
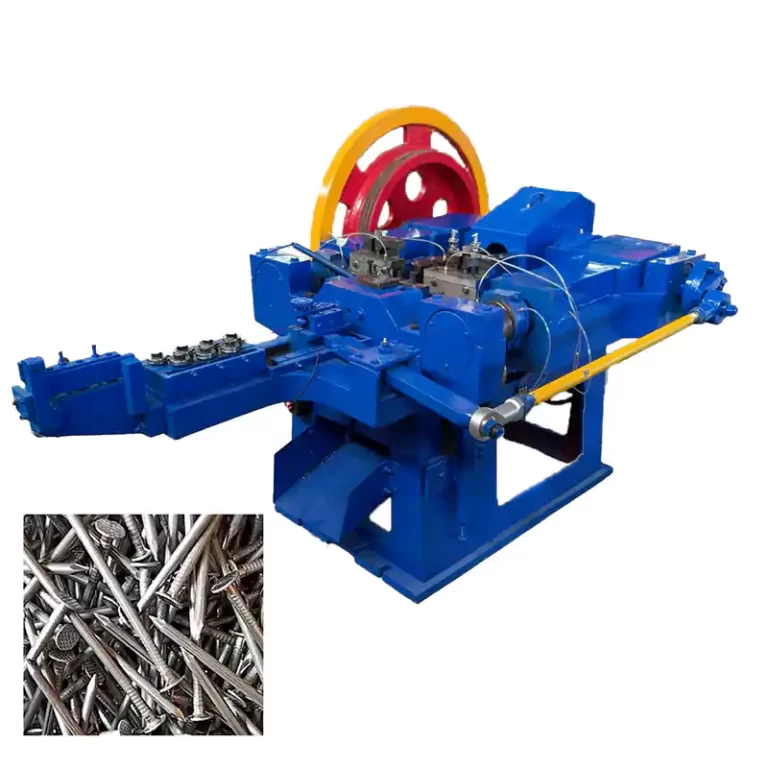
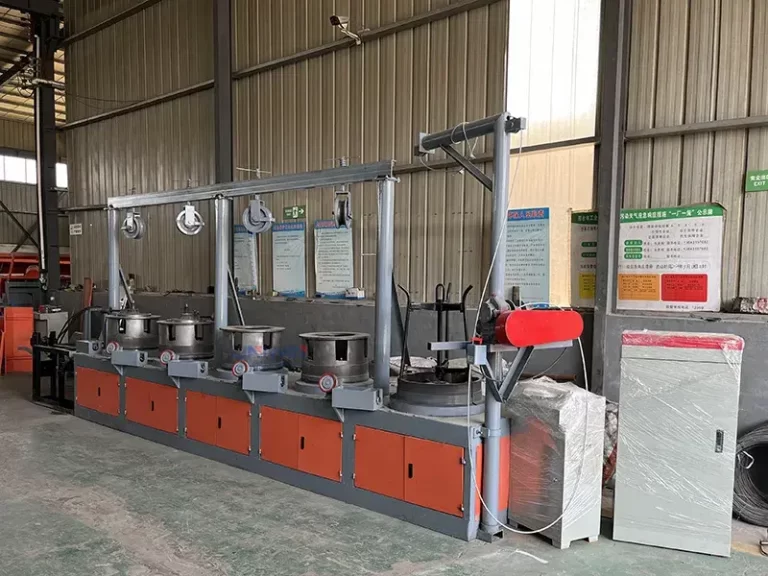
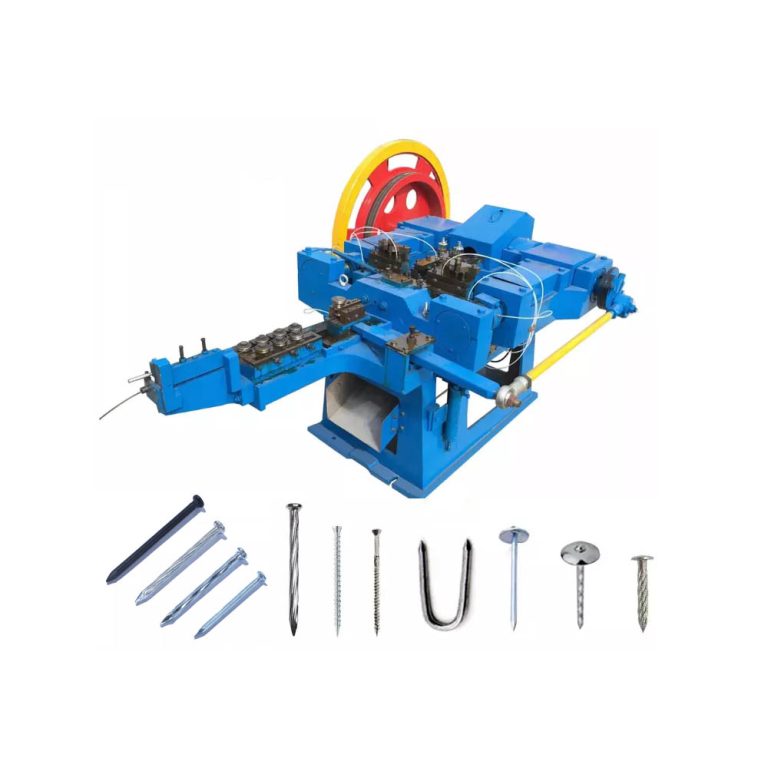
Metal wire drawing machine is used in the manufacturing sector to produce thin steel wires from thicker rods or wires. This process is critical in various industries, including making steel nails, construction, automotive, and electronics, due to the demand for precise and strong steel wires in these applications.
Metal wire drawing machine is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, enabling the production of high-quality steel wires essential for numerous applications. Its efficiency, precision, and ability to produce wires with excellent mechanical properties make it invaluable in industries ranging from construction to aerospace. Understanding its operation and benefits can help industries optimize their production processes and enhance the quality of their products.
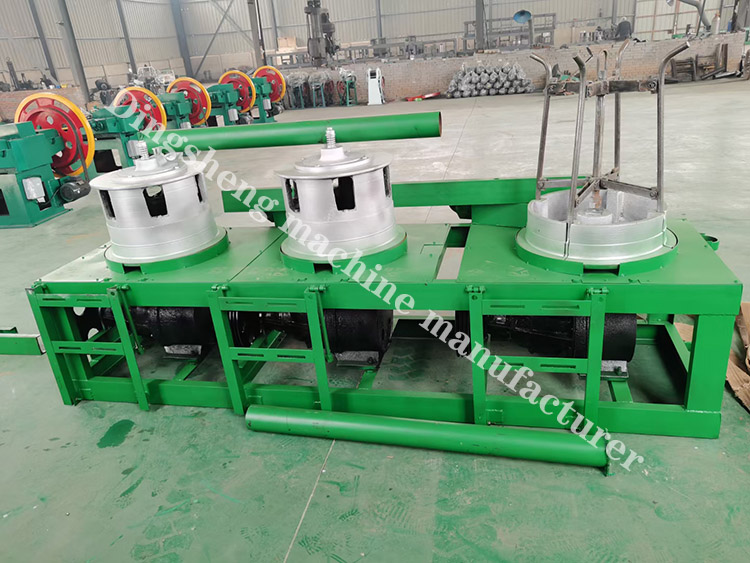

How to operate metal wire drawing machine
Metal wire drawing machine process involves pulling a steel wire through a series of dies or drawing plates, each of which reduces the diameter of the wire incrementally. The process can be summarized in the following steps:
- Preparation of Raw Material: Steel rods or wires are cleaned to remove any scale or rust and then pre-coated with a lubricant to facilitate the drawing process.
- Drawing: The wire is pulled through a sequence of progressively smaller dies. Each die decreases the wire’s diameter, elongating it while maintaining its volume.
- Annealing: Depending on the material and application, the drawn wire may undergo annealing, a heat treatment process that relieves internal stresses and improves ductility.
- Finishing: The wire is finished by applying coatings or further treatments to enhance its properties, such as corrosion resistance or electrical conductivity.
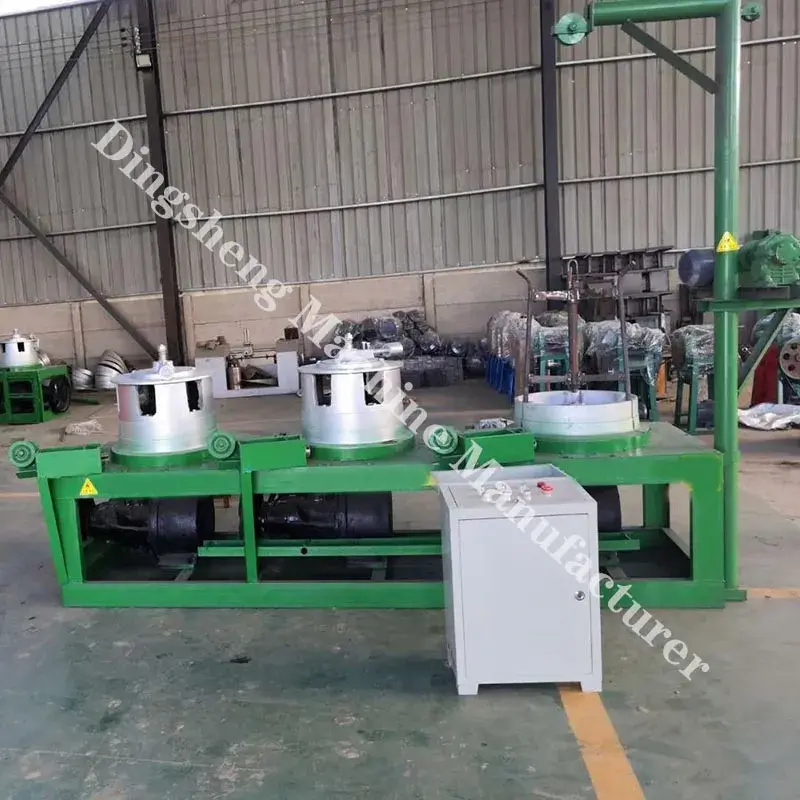
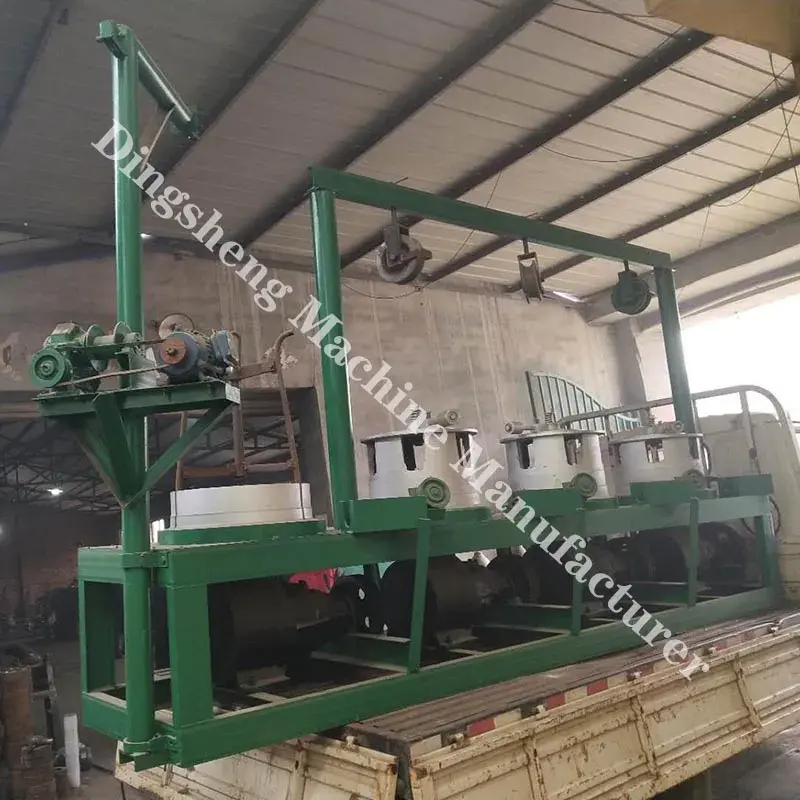
Main components of metal wire drawing machine
- Pay-off Unit: This unit holds the steel rod or wire and feeds it into the drawing machine.
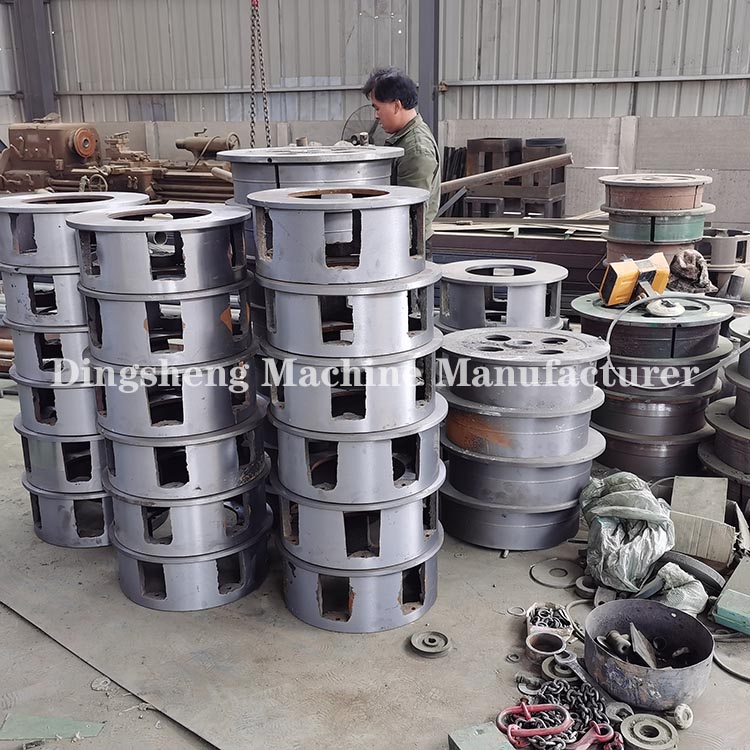
- Drawing Dies: Made from hard materials like tungsten carbide or diamond, these dies progressively reduce the diameter of the wire.
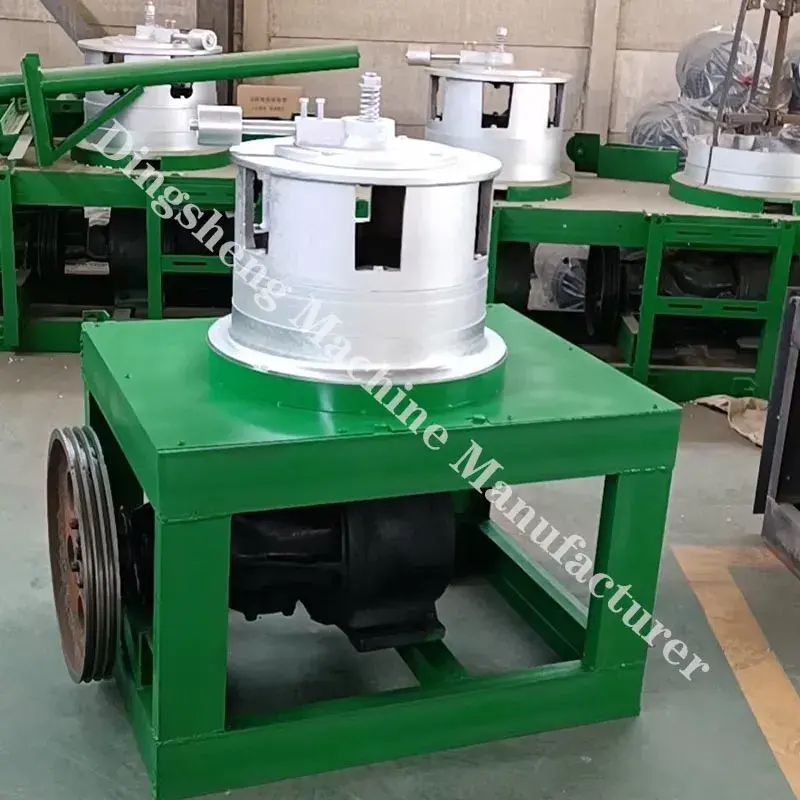
- Drawing Blocks: These are motor-driven capstans or drums that pull the wire through the dies with controlled tension.
- Lubrication System: Ensures continuous lubrication of the wire and dies to reduce friction and wear.
- Annealing Unit: (Optional) A furnace or induction heating system to heat-treat the wire during or after the drawing process.
- Take-up Unit: Collects the finished wire onto spools or coils for further processing or shipping.
Wire drawing dies: steel wire diameter’s change is finished by wire drawing dies.
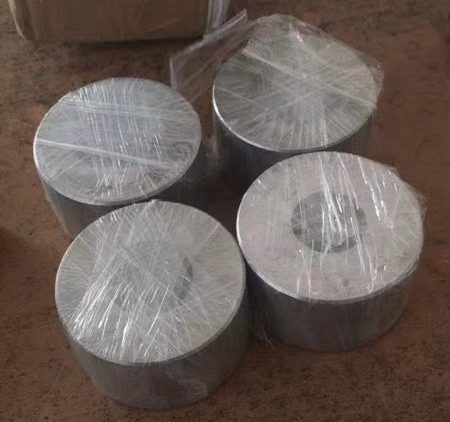

Drawing blocks (550 mm)